Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Hirata, Yuho; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Kai, Takeshi
no journal, ,
Track-structure calculation, a method to simulate every secondary electron production reaction explicitly, has been extensively used as an important techniques in various fields such as radiation biology, material irradiation effect, and radiation detection. The authors have developed and implemented track-structure models to the general-purpose radiation transport simulation code PHITS. This presentation is dedicated to promotion of PHITS in the community of metallurgy as an invited talk of the Japan Institute of Metals and Materials. At first, the whole system of track-structure calculation, composed of the high-precision models optimized for specific materials such as water and semiconductor and generalized models applicable to wider variety of materials, is explained. In metals, electrons are quickly diffused, therefore the scope of this talk is on the generalized model for protons and ions. Its capability to calculate the amount and spatial arrangement of damage is explained as an example of application.
Toyota, Kodai; Imagawa, Yuya; Onizawa, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Namie, Masanari; Oka, Ryotaro*; Kim, J.-H.*; Yonezawa, Susumu*; Saito, Junichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Imagawa, Yuya; Toyota, Kodai; Onizawa, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Taisei*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Ngo, N. H.*; Yamano, Hidemasa
no journal, ,
Viscosity of molten Ferrum Casting Ductile (FCD) was measured by using a oscillating crucible viscometer. This study confirmed the decrease of the viscosity with increase of Cu content over 1300 degree C, in which FCD melts completely.
Abe, Yosuke; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Okubo, Nariaki; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ukai, Shigeharu
no journal, ,
In Fe-Cr-Al (ODS) alloys being developed as accident tolerant fuel cladding for light water reactors, it is a challenge to understand and predict the precipitation behaviour of the Cr-rich embrittlement phase (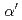 phase), which occurs at relatively low irradiation temperatures, and its effect on mechanical properties. Therefore, in this study, the
phase), which occurs at relatively low irradiation temperatures, and its effect on mechanical properties. Therefore, in this study, the  phase boundary was rationally defined on the alloy state diagram under varying conditions such as temperature and aging time by combining thermal aging experiments on Fe-Cr-Al alloys with systematically varying Cr and Al compositions and machine learning models. The regression model was applied to the 3DAP database to evaluate the relationship between the estimated increase in Vickers hardness and the hardening mechanism due to the
phase boundary was rationally defined on the alloy state diagram under varying conditions such as temperature and aging time by combining thermal aging experiments on Fe-Cr-Al alloys with systematically varying Cr and Al compositions and machine learning models. The regression model was applied to the 3DAP database to evaluate the relationship between the estimated increase in Vickers hardness and the hardening mechanism due to the 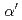 phase. The results suggest that the hardening due to the
phase. The results suggest that the hardening due to the 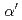 phase can be explained by a particle cutting mechanism.
phase can be explained by a particle cutting mechanism.
Ito, Yuto*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Abe, Eiji*
no journal, ,
Among hcp metals, Zn and Cd, which have high c/a ratios, exhibit kink deformation characterized by crystal rotation under conditions of suppressed basal slip under in-basal compression. Kink deformation has recently attracted attention because it compensates for the plastic deformation of the hcp structure, which has a limited independent slip system, and also contributes to high strength in some Mg alloys. In this study, we evaluated the structural stability of hcp metals under uniaxial compression conditions where basal slip is suppressed, using first-principles calculations of the Phonon dispersion relation and generalized stacking fault energy (GSFE) to understand the kink deformation mechanism.
Wakai, Eiichi; Noto, Hiroyuki*; Shibayama, Tamaki*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishida, Taku*; Sato, Koichi*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; Takahashi, Toshiharu*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
In recent years, it has been reported that high-entropy alloys (HEA) have high strength but good ductility, and they are being researched and developed by cutting-edge research institutions around the world with the aim of finding various applications in progress. In this study, we considered several Fe-based, W-based, and Ti-based HEAs, excluding Co and Ni elements, in order to aim for use in high radiation fields and considering low-activation properties. These materials mainly have a bcc crystal structure and were fabricated using a melting method and their material properties were evaluated. As a result, it was found that Fe-based HEA has properties that exceed the hardness of pure W and has excellent irradiation resistance. In addition, a Ti-based HEA that can be subjected to high-temperature forging and high-temperature rolling has been found, and evaluation of the optimal heat treatment temperature is progressing. The hardness of W-based HEA increased through Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) treatment, and it was found to have the world's highest hardness among HEA materials.
 samples irradiated with swift heavy ions
samples irradiated with swift heavy ionsIshikawa, Norito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Ogawa, Hiroaki
no journal, ,
Unique Nanostructure is found at the Edge of SiO Samples Irradiated with Swift Heavy Ions. Previous studies show that in many ceramics structure inside the iontracks are homogeneous. I the present study, concentric double structure is found at the edge of SiO
Samples Irradiated with Swift Heavy Ions. Previous studies show that in many ceramics structure inside the iontracks are homogeneous. I the present study, concentric double structure is found at the edge of SiO . Since the previous studies of SiO
. Since the previous studies of SiO show that even in SiO
show that even in SiO homogeneous ion track structure is reported, the present result contradict the previous ones. Actually homogeneous ion track structure is observed in thick part of the sample, while double structure is observed in thin part of the sample. At the edge of the sample, concentric double structure changes into mouth-opeing structure which is unique to SiO
homogeneous ion track structure is reported, the present result contradict the previous ones. Actually homogeneous ion track structure is observed in thick part of the sample, while double structure is observed in thin part of the sample. At the edge of the sample, concentric double structure changes into mouth-opeing structure which is unique to SiO .
.
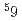 Co NMR on high-entropy alloy FeCoNiCrPd
Co NMR on high-entropy alloy FeCoNiCrPdChudo, Hiroyuki; Suzuki, Kazuya; Okamoto, Norihiko*; Ichitsubo, Tetsu; Takanashi, Koki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ohigashi, Jun*; Kawamura, Kenichi*; Ueda, Mitsutoshi*; Irisawa, Eriko; Komatsu, Atsushi
no journal, ,
In order to apply zirconium alloys and their oxide films to oxygen sensors, high temperature oxidation experiments were conducted on Zr-63 at.%Al, Zr-39 at.%Al, and Zr-31 at.%Y alloys. The oxidation behavior of these alloys was observed, and the oxide ion conductivity was examined by measuring the electromotive force of the oxide films of the alloys whose oxidation inhibition was confirmed. Zr-39 at.% Al and Zr-31 at.% Y alloys. On the other hand, a thin, uniform, dense zirconium oxide film was formed for the Zr-63 at.%Al alloy. The electromotive force (EMF) of this oxide film was measured in a gas of known oxygen concentration, but it was smaller than the expected EMF, and the oxide ion conductivity was not sufficient.